Pigmentation
Understanding Pigmentation
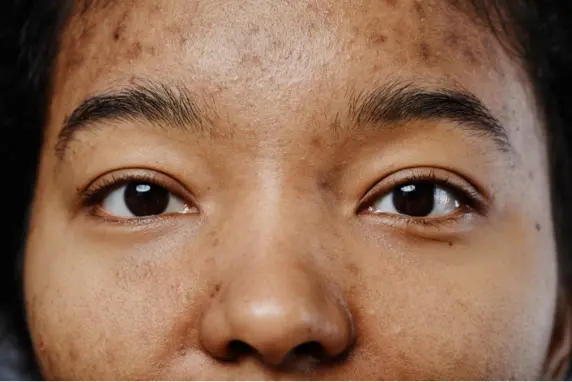
Hyperpigmentation, or uneven skin tone, is a condition where patches of skin become darker due to an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin and hair color. Commonly perceived as “aged skin,” hyperpigmentation can make skin appear older and affect overall complexion. Dark patches and spots may result from various factors, including sun exposure, pollution, hormones, and skin injuries.
Causes of Uneven Skin Tone
-
Sun Exposure: Prolonged UV exposure triggers excess melanin production as the skin tries to protect itself, resulting in brown spots and an uneven tone.
-
Pollution: Air pollution, especially from traffic, can penetrate the skin and contribute to dark spots, particularly on the face, due to oxidative stress.
-
Hormones: Hormone-related hyperpigmentation, known as melasma, commonly affects women during pregnancy or while using contraceptives. It can also be triggered by certain cosmetics or medications.
-
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation: This type of pigmentation occurs after skin injury or inflammation, such as from acne lesions or scarring, which can lead to dark spots in the affected areas.
Need Help
Frequently Asked Questions about Pigmentation
Here are some common questions about hyperpigmentation, its causes, and effective treatments.
1. What is hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation refers to darkening of the skin due to excess melanin production, often seen as patches or spots that give an uneven tone.
2. How does sun exposure affect pigmentation?
UV rays stimulate melanin production as a protective response, which can lead to brown spots and uneven skin tone, especially with prolonged sun exposure.
3. What is melasma?
Melasma is hormone-related pigmentation, often triggered by pregnancy or contraceptives. It's commonly known as the “mask of pregnancy” due to its appearance on the face.
4. How can pollution cause pigmentation?
Pollution particles can penetrate the skin and cause oxidative stress, leading to the formation of dark spots, especially in exposed areas like the face.
5. What is post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation?
This type of pigmentation occurs after skin injury or inflammation, such as acne or scarring, leaving dark patches where the skin has healed.
6. Are there treatments for hyperpigmentation?
Yes, treatments like chemical peels, laser therapy, and topical agents can help reduce hyperpigmentation. Consulting a dermatologist for personalized care is recommended.
7. Can lifestyle changes help prevent pigmentation?
Using sunscreen, avoiding direct sun exposure, and maintaining a balanced skincare routine can help minimize the risk of hyperpigmentation.
8. Who is more prone to pigmentation issues?
People with darker skin tones, those with a family history of pigmentation issues, and individuals frequently exposed to the sun are more prone to pigmentation.
What Our Clients Say
Contact Us
Send A Message
If you want to ask anything just fill in the form below and send us.
